Products Description
Alloy 2205 (UNS S32305/S31803) is a duplex stainless steel plate that offers a combination of excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and good impact toughness. Here are some key points about Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate:Alloy 2205 consists of 22% chromium, 3% molybdenum, 5-6% nickel, and nitrogen as alloying elements.The duplex microstructure of the alloy, with a balanced combination of ferrite and austenite phases, contributes to its unique properties.Alloy 2205 provides superior pitting and crevice corrosion resistance compared to austenitic stainless steels such as 316L or 317L in a wide range of corrosive media.It exhibits excellent resistance to general corrosion and localized corrosion, making it suitable for applications in aggressive environments.Alloy 2205 offers high strength, allowing it to withstand heavy loads and pressures.It demonstrates excellent impact toughness, making it resistant to brittle fracture even at low temperatures.The alloy possesses high corrosion and erosion fatigue properties, making it suitable for applications subject to cyclic loading and corrosive environments.Alloy 2205 has lower thermal expansion compared to austenitic stainless steels, which can be beneficial in certain applications.It also exhibits higher thermal conductivity, facilitating efficient heat transfer.Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate finds applications in various industries, including chemical processing, oil and gas, pulp and paper, and marine environments. It is commonly used in equipment such as pressure vessels, heat exchangers, pipes, and structural components.As always, it's important to consider specific operating conditions and consult with materials engineers or alloy manufacturers for precise guidance on the use, fabrication, and compatibility of Alloy 2205 in particular applications and environments.
Applications
- Pressure vessels, tanks, piping, and heat exchangers in the chemical processing industry
- Piping, tubing, and heat exchangers for the handling of gas and oil
- Effluent scrubbing systems
- Pulp and paper industry digesters, bleaching equipment, and stock-handling systems
- Rotors, fans, shafts, and press rolls requiring combined strength and corrosion resistance
- Cargo tanks for ships and trucks
- Food processing equipment
- Biofuels plants
Standards
ASTM/ASME...........A240 UNS S32205/S31803EURONORM...........1.4462 X2CrNiMoN 22.5.3
AFNOR...................Z3 CrNi 22.05 AZ
DIN.........................W. Nr 1.4462
General Properties
Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate offers a range of advantageous properties. Here are some additional details:Composition:Alloy 2205 is composed of 22% chromium, 3% molybdenum, 5-6% nickel, and nitrogen as alloying elements.The duplex microstructure, consisting of both ferrite and austenite phases, contributes to its unique properties.
Corrosion Resistance:
Alloy 2205 provides superior pitting and crevice corrosion resistance compared to austenitic stainless steels like 316L or 317L in most corrosive environments.
It exhibits excellent resistance to general corrosion and localized corrosion, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Mechanical Properties:
The yield strength of Alloy 2205 is approximately twice that of austenitic stainless steels, allowing for weight savings and cost competitiveness.
The alloy possesses high strength and excellent impact toughness, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Fatigue Properties:
Alloy 2205 offers high corrosion and erosion fatigue properties, making it suitable for applications subjected to cyclic loading and corrosive environments.
Thermal Properties:
Alloy 2205 has lower thermal expansion and higher thermal conductivity compared to austenitic stainless steels, which can be advantageous in certain applications.
Temperature Range:
Alloy 2205 is particularly suitable for applications within the temperature range of -50°F to +600°F (-46°C to +316°C).While the alloy can be considered for temperatures outside this range, some restrictions may apply, especially for welded structures.
Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate finds applications in various industries, including chemical processing, oil and gas, pulp and paper, and marine environments. It is commonly used in equipment such as pressure vessels, heat exchangers, pipes, and structural components.
Corrosion Resistance
General Corrosion
Because of its high chromium (22%), molybdenum (3%), and nitrogen (0.18%) contents, the corrosion resistance properties of 2205 duplex stainless steel plate are superior to that of 316L or 317L in most environments.
Localized Corrosion Resistance
The chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen in 2205 duplex stainless steel plate also provide excellent resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion even in very oxidizing and acidic solutions.
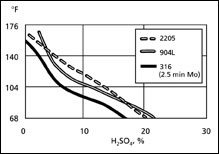
Stress Corrosion Resistance
The duplex microstructure is known to improve the stress corrosion cracking resistance of stainless steels.
Chloride stress corrosion cracking of austenitic stainless steels can occur when the necessary conditions of temperature, tensile stress, oxygen, and chlorides are present. Since these conditions are not easily controlled, stress corrosion cracking has often been a barrier to utilizing 304L, 316L, or 317L.
Corrosion Fatigue Resistence
Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate combines high strength and high corrosion resistance to produce high corrosion fatigue strength. Applications in which processing equipment is subject to both an aggresively corrosive enviroment and to cycle loading can benefit from the properties of 2205 duplex stainless steel plate.
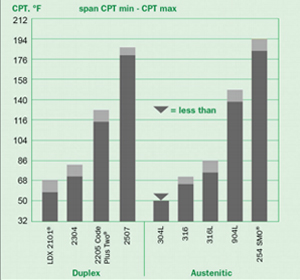
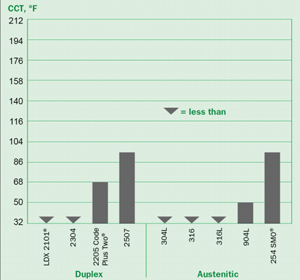
General Corrosion in Wet Process Phosphoric Acids
|
Corrosion Rate, ipy |
||||||||
|
Grade |
Solution A, 1401/4F |
Solution B, 1201/4F |
||||||
|
2205 |
3.1 |
3.9 |
||||||
|
316L |
>200 |
>200 |
||||||
|
904L |
47 |
6.3 |
||||||
|
Composition, wt% |
||||||||
|
P2O5 |
HCl |
HF |
H2SO4 |
Fe2O3 |
Al203 |
SiO2 |
CaO |
MgO |
|
Sol A 54.0 |
0.06 |
1.1 |
4.1 |
0.27 |
0.17 |
0.10 |
0.20 |
0.70 |
|
Sol B 27.5 |
0.34 |
1.3 |
1.72 |
0.4 |
0.001 |
0.3 |
0.02 |
— |
Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance
|
|
Boiling |
Wick |
Boiling |
|
Grade |
42% MgCl2 |
Test |
25% NaCl |
|
2205 |
F |
P |
P |
|
254 SMO® |
F |
P |
P |
|
Type 316L |
F |
F |
F |
|
Type 317L |
F |
F |
F |
|
Alloy 904L |
F |
P or F |
P or F |
|
Alloy 20 |
F |
P |
P |
(P = Pass, F = Fail)
Chemical Analysis
Typical Values (Weight %)
|
Carbon |
Chromium |
Nickel |
Molybdenum |
Nitrogen |
Others |
|
0.020 |
22.1 |
5.6 |
3.1 |
0.18 |
S=0.001 |
|
PREN = [Cr%] = 3.3 [Mo%] = 16 [N%] ≥ 34 |
|||||
Physical Properties
|
Temperature °F |
|
68 |
212 |
392 |
572 |
|
Density |
lb/in3 |
0.278 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Modulus of Elasticity |
psi x 106 |
27.6 |
26.1 |
25.4 |
24.9 |
|
Linear Expansion (68°F-T) |
10-6/°F |
— |
7.5 |
7.8 |
8.1 |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
Btu/h ft°F |
8.7 |
9.2 |
9.8 |
10.4 |
|
Heat Capacity |
Btu/lb ft°F |
0.112 |
0.119 |
0.127 |
0.134 |
|
Electrical Resistivity |
Ωin x 10-6 |
33.5 |
35.4 |
37.4 |
39.4 |
Mechanical Properties
|
|
ASTM A 240 |
Typical |
|
Yield Strength 0.2%, ksi |
65 min. |
74 |
|
Tensile Strength, ksi |
90 min. |
105 |
|
Elongation, % |
25 min. |
30 |
|
Hardness RC |
32 max. |
19 |
Tensile Properties at Elevated Temperatures
|
Temperature °F |
122 |
212 |
392 |
572 |
|
Yield Strength 0.2%, ksi |
60 |
52 |
45 |
41 |
|
Tensile Strength, ksi |
96 |
90 |
83 |
81 |
Structure
The chemical analysis of 2205 duplex stainless steel plate is optimized to obtain a typical 50 a/ 50 g microstructure after solution annealing treatment at 1900°/1922°F (1040°/1080°C).
Chloride Pitting Resistance
The pitting resistance of an austenitic stainless steel can be related directly to alloy composition, where chromium, molybdenum and nitrogen are a weight %. The Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN) uses the following formula to measure an alloy's relative pitting resistance - the higher the number, the better the pitting resistance.
Processing
Hot Forming
Forming below 600°F is recommended whenever possible. When hot forming is required, the workpiece should be heated uniformly and worked in the range of 1750 to 2250°F. Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate is quite soft at these temperatures and is readily formed. Above this range, 2205 is subject to hot tearing. Immediately below this range, the austenite becomes substantially stronger than the ferrite and may cause cracking, a particular danger to “cold” edges. Below 1700°F there can be rapid formation of intermetallic phases because of the combination of temperature and deformation. Whenever hot forming is done, it should be followed by a full solution anneal at 1900°F minimum and rapid quench to restore phase balance, toughness, and corrosion resistance. Stress relieving is not required or recommended; however, if it must be performed, the material should receive a full solution anneal at 1900°F minimum, followed by rapid cooling or water quenching.
Cold Forming
Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate is readily sheared and cold formed on equipment suited to working stainless steels. However, because of the high strength and rapid work hardening of 2205 duplex stainless steel plate, forces substantially higher than those for austenitic steels are required to cold form it. Also because of the high strength, a somewhat larger allowance must be made for springback.
Heat Treatment
Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate should be annealed at 1900°F minimum, followed by rapid cooling, ideally by water quenching. This treatment applies to both solution annealing and stress relieving. Stress relief treatments at any lower temperature carry the risk of precipitation of detrimental intermetallic or nonmetallic phases.
Machinability
With high-speed steel tooling, 2205 duplex stainless steel plate may be machined at the same feeds and speeds as Alloy 316L. When carbide tooling is used, cutting speeds should be reduced by about 20% relative to the speeds for Alloy 316L. Powerful machines and rigid mounting of tools and parts are essential.
Welding
Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate possesses good weldability. The goal of welding 2205 is that the weld metal and heat-affected zone (HAZ) retain the corrosion resistance, strength, and toughness of the base metal. The welding of 2205 is not difficult, but it is necessary to design welding procedures that lead to a favorable phase balance after welding and will avoid precipitation of detrimental intermetallic or nonmetallic phases.
Alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel plate can be welded by: GTAW (TIG); GMAW (MIG); SMAW ("stick" electrode); SAW; FCW; and PAW.
