Alloy 2304 (UNS S32304) is a duplex stainless steel with a composition that includes 23% chromium, 4% nickel, and is molybdenum-free. Here are some key points about Alloy 2304:
Corrosion Resistance:
Alloy 2304 exhibits corrosion resistance properties similar to those of 316L austenitic stainless steel.
It provides good resistance to a wide range of corrosive environments, including chloride-containing solutions.
Mechanical Properties:
Compared to austenitic grades such as 304L and 316L, Alloy 2304 offers higher mechanical strength, including yield strength.
The increased strength allows for weight savings in applications, particularly in properly designed pressure vessel applications.
Duplex Microstructure:
Alloy 2304 has a duplex microstructure consisting of a balanced mix of ferrite and austenite phases.
This microstructure contributes to the alloy's combination of corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.Alloy 2304 is commonly used in various industries, including chemical processing, oil and gas, and marine environments. It finds applications in equipment such as pressure vessels, heat exchangers, piping systems, and structural components.
Applications
- Generally where 304 and 316L are used
- Pulp and paper industry (chip storage tanks, white and black liquor tanks, digestors)
- Caustic solutions, organic acids (SCC resistance)
- Food industry
- Pressure vessels (weight savings)
- Mining (abrasion/corrosion)
Standards
ASTM/ASME.......... A240 - UNS S32304
EURONORM...........1.4362 - X2 Cr Ni 23.4
AFNOR...................Z3 CN 23.04 Az
DIN.........................W. Nr 1.4362
Alloy 2304 is a 23% chromium, 4% nickel, molybdenum-free duplex stainless steel. The Alloy 2304 has corrosion resistance properties similar to 316L. Furthermore, its mechanical properties, i.e., yield strength, are twice those of 304/316 austenitic grades. This allows the designer to save weight, particularly for properly designed pressure vessel applications.
The alloy is particularly suitable for applications covering the -50°C/+300°C (-58°F/572°F) temperature range. Lower temperatures may also be considered but need some restrictions, particularly for welded structures.
With its duplex microstructure and low nickel and high chromium contents, the alloy has improved stress corrosion resistance properties compared to 304 and 316 austenitic grades.
General Corrosion
Because of its high chromium content (23%) the corrosion resistance properties of 2304 are almost equivalent to those of 316L.

Corrosion resistance in different organic acids
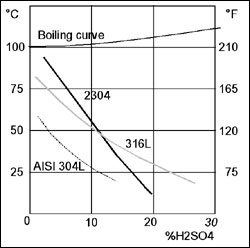
Corrosion resistance to stagnant sulfuric acid (0,3 mm/year)
Localized Corrosion Resistance
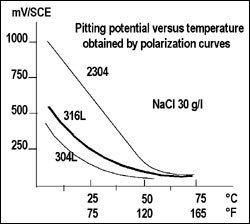
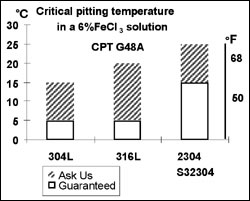
The 23% chromium and 0.1% nitrogen additions explain why 2304 duplex stainless steel behaves much better than Alloy 316L when considering pitting and crevice corrosion resistance.
Stress Corrosion Resistance
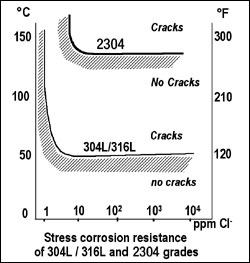
Stress corrosion resistance test results in chloride containing aqueous solutions ((8ppm 02) PH =7, >1000 h, applied stresses higher than the yield strength) show that Alloy 2304 outperforms Alloys 304L and 316L, due to its high chromium additions and low nickel contents.
This is a typical feature of duplex stainless steels. Alloy 2205 performs still better than 2304 in similar conditions.
Other Corrosion Resistance Properties
Alloy 2304 duplex stainless steel successfully passes most of the standard IC test procedures such as ASTM, A262E, and C tests. Its corrosion rate in boiling nitric acid (65%) is higher than that of Alloy 316L. Due to its high yield strength, the alloy performs well in abrasion/corrosion applications.
Typical Values (Weight %)
|
Carbon
|
Chromium
|
Nickel
|
Molybdenum
|
Nitrogen
|
Others
|
|
0.020
|
23
|
4
|
0.2
|
0.1
|
S=0.001
|
|
PREN = [Cr%] = 3.3 [Mo%] = 16 [N%] ≥ 24
|
Physical Properties
Density
7,800 kg/m3 - 0.28 lb/in3
|
Interval
Temper
°C
|
Thermal
expansion
ax10M-bK-1
|
°C
|
Resistivity
(μ_ cm)
|
Thermal
conductivity
(W.m-1.K-1)
|
Specific
heat
(J.kg-1.K-1
|
Young
modulus
E
(GPa)
|
Shear
modulus
G
(GPa)
|
|
20-100
|
13
|
20
|
80
|
17
|
450
|
200
|
75
|
|
20-100
|
13
|
100
|
92
|
18
|
500
|
190
|
73
|
|
20-200
|
13.5
|
200
|
100
|
19
|
530
|
180
|
70
|
|
20-300
|
14
|
300
|
105
|
20
|
560
|
170
|
67
|
Mechanical Properties
Tensile Properties (Minimum Values)
|
°C
|
Rp 0.2
MPa
|
Rp 1.0
MPa
|
Rp 1.0
MPa
|
°F
|
YS 0.2%
Offset KSI
|
YS 0.1%
Offset KSI
|
UTS
KSI
|
Elongation
%
|
|
20
|
400
|
440
|
600
|
68
|
58
|
64
|
87
|
25
|
|
100
|
330
|
365
|
570
|
212
|
48
|
53
|
83
|
25
|
|
200
|
280
|
310
|
530
|
392
|
41
|
45
|
77
|
20
|
|
300
|
230
|
260
|
490
|
572
|
33
|
38
|
71
|
20
|
Values obtained for hot rolled plates (th ≤ 2"). Alloy 2304 must not be used for a long time at temperatures higher than 300°C (572°F), where precipitation hardening phenomenon occurs.
Toughness Values (KCV Minimum Values)
|
Temp.
|
-50°C
|
+20°C
|
-60°F
|
+70°F
|
|
Single
|
75 J/cm_
|
90 J/cm_
|
54 ft. lbs
|
65 ft. lbs
|
|
Average (5)
|
90 J/cm_
|
150 J/cm
|
65 ft. lbs
|
87 ft. lbs
|
Hardness (Typical Values)
|
Average (5)
|
HV10 180-230
|
HB : 180-230
|
HRC _ 20
|
Structure
The chemical analysis of 2304 is optimized to obtain a typical 50 a / 50 g microstructure after solution annealing treatment at 950°/1050°C (1742°/1922°F).
The microstructure of 2304 duplex is very stable compared to molybdenum-containing duplex stainless steels. Intermetallic phases are present only after 10 hours holding time in the 750°/850°C (1382°/1562°F) temperature range. Copper additions to 2304 grade, when specified, increase the hardness of the steel after heat treatment in the 350°/500°C (662°/932°F) temperature range.
Processing
Hot Forming
Hot forming must be performed in the 1150/900°C (2100/1650°F) temperature range. After forming, a new solution annealing treatment is recommended in the 950°/1050°C (2100°/1650°F) temperature range to fully restore corrosion resistance properties and mechanical properties. Parts formed with 2304 must be supported carefully during heating to avoid creep deformation.
Cold Forming
Alloy 2304 may be cold formed without any problem. The same equipment as used for the cold forming of 304L and 316L grades can be used. Due to its higher mechanical properties, including the yield strength, higher stresses are required for cold forming. A final solution annealing heat treatment is also recommended after cold forming in order to restore the mechanical and corrosion resistance properties, as decribed in ‘hot forming.’
Descaling
Alloy 2304 duplex exhibits improved machinability properties particularly when considering drilling. Its behavior is equivalent to that of 316LEZ*. Furthermore, 2304 has better corrosion resistance and cleanliness properties as no sulphur additions are necessary. Localized corrosion resistance behavior is improved.
*316LEZ is a 316L type grade with improved machinability properties.